算法原理
在生物神经网络中,每个神经元与其他神经元相连,当它兴奋时,就会向相连的神经元发送化学物质,从而改变这些神经元内的电位。如果某神经元的电位超过了一个阈值,那么它就会被激活,从而兴奋起来,继续向其他神经元发送化学物质,从而将信号逐层传递下去。
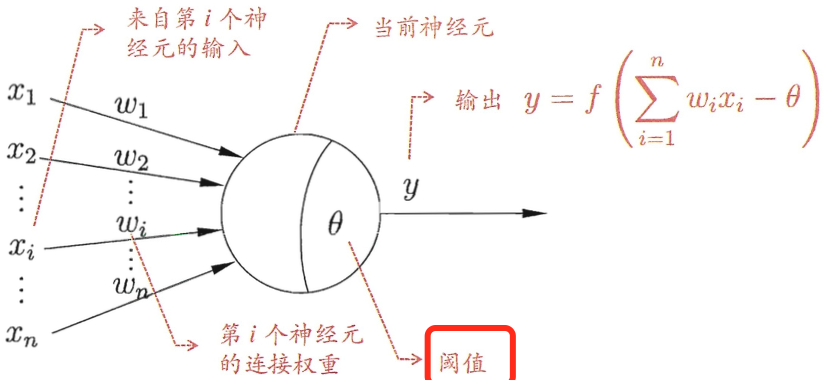 如上所示,神经元接收到来自n个其他神经元传递过来的输入信号,并且每个输入信号带有一定的权重,神经元接收到的总输入值将与神经元的阈值比较,然后通过激活函数处理以产生神经元的输出(决定是否被激活)。
如上所示,神经元接收到来自n个其他神经元传递过来的输入信号,并且每个输入信号带有一定的权重,神经元接收到的总输入值将与神经元的阈值比较,然后通过激活函数处理以产生神经元的输出(决定是否被激活)。
 把许多个这样的神经元按照一定的层次结构连接起来,就得到了神经网络。
把许多个这样的神经元按照一定的层次结构连接起来,就得到了神经网络。
之所以又把DNN叫多层感知机Multi-Layer Perceptron,是因为我们的逻辑回归实际上就是一个一层的神经网络,只有输入层和输出层,没有隐藏层,这就是一个感知机,所以感知机本质上还是一个对数线性模型,无法处理非线性问题,但是多层感知机(含有1到多个隐藏层的神经网络)可以,可以证明,只需一个包含足够多神经元的隐层,MLP就能以任意精度逼近任意复杂度的连续函数。
神经网络(DNN、CNN、RNN等)的训练都是通过反向传播(backpropagation)完成的,反向传播是梯度下降算法的一种特殊实现,是神经网络专用的参数更新算法,参数的更新过程也是通过梯度下降的公式推到计算而来的。(推导过程详见:《机器学习》周志华第5.3节):
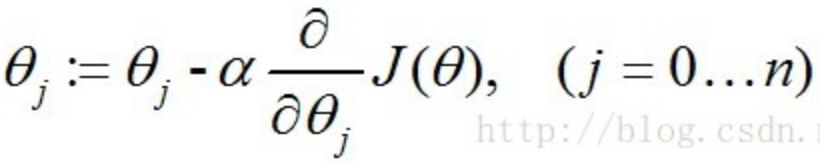 反向传播最终是根据偏误差反向传递。假设我们取激活函数为Sigmoid,Oj代表每一个神经元(隐藏层和输出层)的输出值,Oi为每个神经元的实际值,那么我们可以计算每个神经元的偏误差:
对于输出层:
反向传播最终是根据偏误差反向传递。假设我们取激活函数为Sigmoid,Oj代表每一个神经元(隐藏层和输出层)的输出值,Oi为每个神经元的实际值,那么我们可以计算每个神经元的偏误差:
对于输出层:
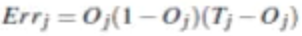 对于隐藏层:
对于隐藏层:
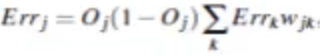 权重更新:
权重更新:
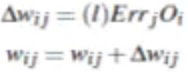 偏向更新:
偏向更新:
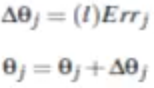 下面通过一个实际例子来说明反向传播的具体过程,假设下面的两层神经网络最终的输出T = 1:
下面通过一个实际例子来说明反向传播的具体过程,假设下面的两层神经网络最终的输出T = 1:
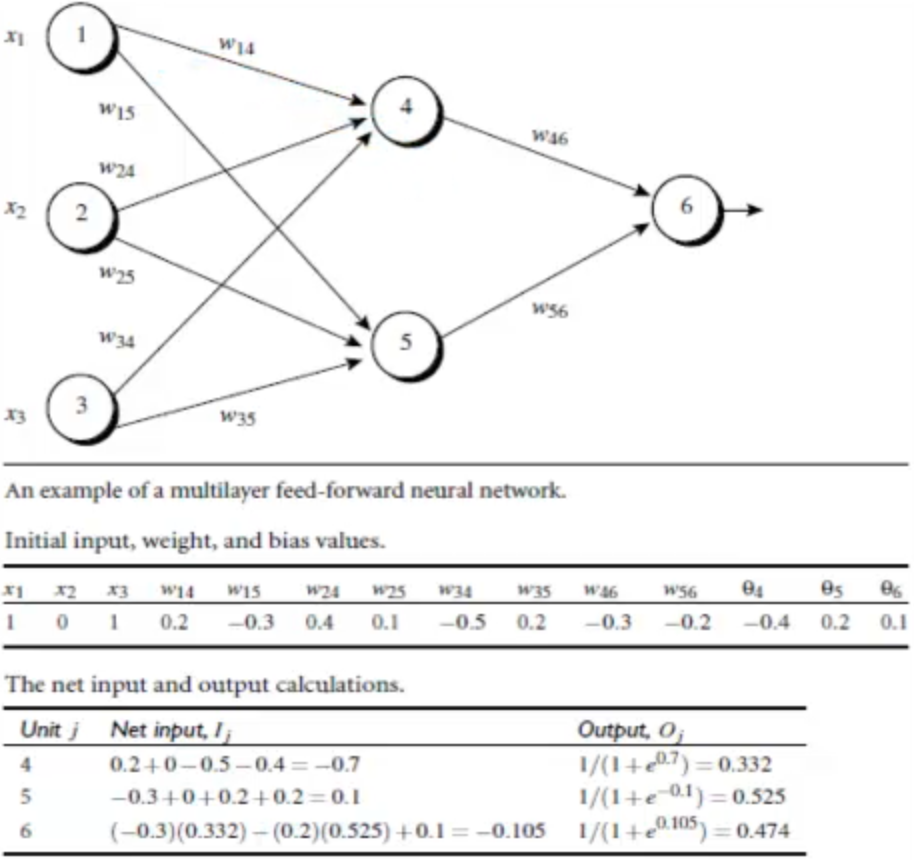
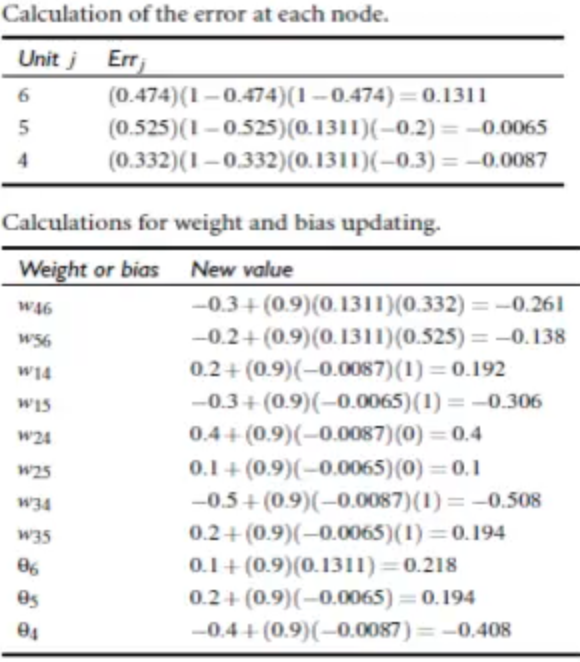 以上就是通过backpropagation进行第一轮神经网络训练的全部过程,参数更新完成后,再带入下一个样本点,继续按照一模一样的方式进行后面一轮的迭代更新。
上面的更新过程叫做标准BP算法,即每次传入单个样本进行参数更新,如果每次传入mini-batch数据,就是累积BP算法,这时每个神经元Err的计算就是所有样本Err的平均值。
以上就是通过backpropagation进行第一轮神经网络训练的全部过程,参数更新完成后,再带入下一个样本点,继续按照一模一样的方式进行后面一轮的迭代更新。
上面的更新过程叫做标准BP算法,即每次传入单个样本进行参数更新,如果每次传入mini-batch数据,就是累积BP算法,这时每个神经元Err的计算就是所有样本Err的平均值。
模型训练
sklearn版
代码地址 https://github.com/qianshuang/ml-exp
def train():
print("start training...")
# 处理训练数据
train_feature, train_target = process_file(train_dir, word_to_id, cat_to_id) # 词频特征
# train_feature, train_target = process_tfidf_file(train_dir, word_to_id, cat_to_id) # TF-IDF特征
# 模型训练
model.fit(train_feature, train_target)
def test():
print("start testing...")
# 处理测试数据
test_feature, test_target = process_file(test_dir, word_to_id, cat_to_id)
# test_feature, test_target = process_tfidf_file(test_dir, word_to_id, cat_to_id) # 不能直接这样处理,应该取训练集的IDF值
test_predict = model.predict(test_feature) # 返回预测类别
# test_predict_proba = model.predict_proba(test_feature) # 返回属于各个类别的概率
# test_predict = np.argmax(test_predict_proba, 1) # 返回概率最大的类别标签
# accuracy
true_false = (test_predict == test_target)
accuracy = np.count_nonzero(true_false) / float(len(test_target))
print()
print("accuracy is %f" % accuracy)
# precision recall f1-score
print()
print(metrics.classification_report(test_target, test_predict, target_names=categories))
# 混淆矩阵
print("Confusion Matrix...")
print(metrics.confusion_matrix(test_target, test_predict))
if not os.path.exists(vocab_dir):
# 构建词典表
build_vocab(train_dir, vocab_dir)
categories, cat_to_id = read_category(test_dir)
words, word_to_id = read_vocab(vocab_dir)
# kNN
# model = neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier()
# decision tree
# model = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
# random forest
# model = ensemble.RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10) # n_estimators为基决策树的数量,一般越大效果越好直至趋于收敛
# AdaBoost
# model = ensemble.AdaBoostClassifier(learning_rate=1.0) # learning_rate的作用是收缩基学习器的权重贡献值
# GBDT
# model = ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=10)
# xgboost
# model = xgboost.XGBClassifier(n_estimators=10)
# Naive Bayes
# model = naive_bayes.MultinomialNB()
# logistic regression
# model = linear_model.LogisticRegression() # ovr
# model = linear_model.LogisticRegression(multi_class="multinomial", solver="lbfgs") # softmax回归
# SVM
# model = svm.LinearSVC() # 线性,无概率结果
# model = svm.SVC() # 核函数,训练慢
# MLP
model = neural_network.MLPClassifier(max_iter=200, verbose=True, early_stopping=True) # 注意max_iter是epoch数
train()
test()
运行结果:
building vacab...
read_category...
read_vocab...
start training...
Iteration 1, loss = 0.72800690
Validation score: 0.961111
Iteration 2, loss = 0.12962878
Validation score: 0.967778
Iteration 3, loss = 0.06385715
Validation score: 0.973333
Iteration 4, loss = 0.03742299
Validation score: 0.975556
Iteration 5, loss = 0.02495986
Validation score: 0.974444
Iteration 6, loss = 0.01741929
Validation score: 0.974444
Iteration 7, loss = 0.01319729
Validation score: 0.972222
Validation score did not improve more than tol=0.000100 for two consecutive epochs. Stopping.
start testing...
accuracy is 0.971000
precision recall f1-score support
科技 0.98 0.99 0.98 94
家居 0.93 0.94 0.94 89
财经 0.99 0.98 0.99 115
房产 0.94 0.93 0.94 104
教育 0.97 0.96 0.97 104
游戏 0.99 0.98 0.99 104
时政 0.95 0.96 0.95 94
时尚 0.96 0.98 0.97 91
体育 1.00 0.98 0.99 116
娱乐 0.99 1.00 0.99 89
avg / total 0.97 0.97 0.97 1000
Confusion Matrix...
[[ 93 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 84 0 1 2 1 0 1 0 0]
[ 0 0 113 1 0 0 1 0 0 0]
[ 0 3 0 97 0 0 3 1 0 0]
[ 0 1 0 1 100 0 0 2 0 0]
[ 1 0 0 0 1 102 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 1 3 0 0 90 0 0 0]
[ 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 89 0 1]
[ 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 114 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 89]]
tensorflow版
代码地址 https://github.com/qianshuang/dl-exp
class TextCNN(object):
"""文本分类,MLP模型"""
def __init__(self, config):
self.config = config
# 三个待输入的数据
self.input_x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.config.vocab_size], name='input_x')
self.input_y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.config.num_classes], name='input_y')
self.keep_prob = tf.placeholder_with_default(1.0, shape=())
self.log()
def log(self):
with tf.name_scope("score"):
# hidden layer
# 使用truncated_normal(高斯)初始化权重,可以避免大的权重值减慢训练,切记不可用全0初始化,回忆BP原理
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([self.config.vocab_size, 1024], stddev=0.1)) # 隐藏层1024个神经元
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[1024]))
y_conv_1 = tf.matmul(self.input_x, W1) + b1
layer_1 = tf.nn.relu(y_conv_1) # 激活函数
# 以上代码还可以通过下面的方式简化实现:
# y_conv_1 = tf.layers.dense(self.input_x, 1024)
# y_conv_1 = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(self.input_x, 1024, weights_regularizer=tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(scale=0.001))
# output layer
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([1024, self.config.num_classes], stddev=0.1))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[self.config.num_classes]))
y_conv = tf.matmul(layer_1, W2) + b2
self.y_pred_cls = tf.argmax(y_conv, 1) # 预测类别
with tf.name_scope("optimize"):
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=self.input_y, logits=y_conv))
# 优化器
self.optim = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=self.config.learning_rate).minimize(self.loss)
with tf.name_scope("accuracy"):
# 准确率
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(self.input_y, 1), self.y_pred_cls)
self.acc = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
运行结果:
Configuring model...
Loading training data...
Training and evaluating...
Epoch: 1
Iter: 0, Train Loss: 5.4, Train Acc: 8.59%, Val Loss: 5.2, Val Acc: 10.40%, Time: 0:00:02 *
Iter: 10, Train Loss: 0.81, Train Acc: 72.66%, Val Loss: 0.92, Val Acc: 71.60%, Time: 0:00:05 *
Iter: 20, Train Loss: 0.61, Train Acc: 85.16%, Val Loss: 0.42, Val Acc: 87.90%, Time: 0:00:08 *
Iter: 30, Train Loss: 0.48, Train Acc: 85.16%, Val Loss: 0.37, Val Acc: 89.80%, Time: 0:00:12 *
Iter: 40, Train Loss: 0.37, Train Acc: 92.97%, Val Loss: 0.32, Val Acc: 91.60%, Time: 0:00:16 *
Iter: 50, Train Loss: 0.18, Train Acc: 94.53%, Val Loss: 0.23, Val Acc: 94.00%, Time: 0:00:18 *
Iter: 60, Train Loss: 0.17, Train Acc: 96.09%, Val Loss: 0.21, Val Acc: 94.10%, Time: 0:00:23 *
Iter: 70, Train Loss: 0.4, Train Acc: 92.50%, Val Loss: 0.18, Val Acc: 95.60%, Time: 0:00:26 *
Epoch: 2
Iter: 80, Train Loss: 0.026, Train Acc: 99.22%, Val Loss: 0.22, Val Acc: 93.90%, Time: 0:00:29
Iter: 90, Train Loss: 0.02, Train Acc: 100.00%, Val Loss: 0.18, Val Acc: 95.20%, Time: 0:00:31
Iter: 100, Train Loss: 0.02, Train Acc: 99.22%, Val Loss: 0.16, Val Acc: 95.80%, Time: 0:00:35 *
......
Epoch: 6
Iter: 360, Train Loss: 0.0017, Train Acc: 100.00%, Val Loss: 0.14, Val Acc: 96.20%, Time: 0:01:57
Iter: 370, Train Loss: 0.0016, Train Acc: 100.00%, Val Loss: 0.14, Val Acc: 96.10%, Time: 0:01:59
Iter: 380, Train Loss: 0.0016, Train Acc: 100.00%, Val Loss: 0.14, Val Acc: 96.10%, Time: 0:02:02
No optimization for a long time, auto-stopping...
Loading test data...
Testing...
Test Loss: 0.14, Test Acc: 96.30%
Precision, Recall and F1-Score...
precision recall f1-score support
财经 0.98 0.97 0.98 115
娱乐 1.00 0.98 0.99 89
时政 0.93 0.96 0.94 94
家居 0.90 0.93 0.92 89
游戏 1.00 0.97 0.99 104
教育 0.97 0.92 0.95 104
时尚 0.95 0.99 0.97 91
科技 0.99 0.99 0.99 94
房产 0.91 0.92 0.91 104
体育 1.00 0.99 1.00 116
avg / total 0.96 0.96 0.96 1000
Confusion Matrix...
[[112 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0]
[ 0 87 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0]
[ 1 0 90 0 0 0 0 0 3 0]
[ 1 0 0 83 0 1 0 0 4 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 101 1 1 1 0 0]
[ 0 0 1 3 0 96 2 0 2 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 1 90 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 93 0 0]
[ 0 0 3 4 0 0 1 0 96 0]
[ 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 115]]
社群
- QQ交流群

- 微信交流群

- 微信公众号
